Important Articles held on 21st and 22nd June
Habeas corpus
Important Articles held on 21st and 22nd June Article 32 of the Indian Constitution is a fundamental right that grants individuals the right to seek enforcement of their fundamental rights through the Supreme Court of India.
Habeas Corpus It is a Latin term which literally means ‘to I have the body of’ . It is an order issued by the court to a person who has detained another person, to produce the body of the latter before it. The court then examines the cause and legality of detention. It would set the detained person free, if the detention is found to be illegal. Thus, this writ is a bulwark of individual liberty against arbitrary detention.
The writ of habeas corpus can be issued against both public authorities as well as private individuals . The writ, on the other hand, is not issued where the
- detention is lawful
- the proceeding is for contempt of a legislature or a court
- detention is by a competent court, and
- detention is outside the jurisdiction of the court .
Brief explanation of Article 32:
- Article 32 states that an individual has the right to move the Supreme Court of India for the enforcement of fundamental rights when they are violated.
- This article empowers the Supreme Court to issue writs, including habeas corpus, mandamus, prohibition, quo warranto, and certiorari, for the protection of fundamental rights.
- The purpose of Article 32 is to ensure that citizens have an effective and direct remedy when their fundamental rights are infringed upon by the state or any other authority.
- It allows any person, regardless of their citizenship, to approach the Supreme Court directly without having to go through the lower courts first, in cases involving the violation of fundamental rights.
- The Supreme Court has the power to issue directions, orders, or writs as necessary to protect and enforce fundamental rights.
- Article 32 is considered a cornerstone of the Indian Constitution and plays a crucial role in upholding the rights and liberties of individuals.
- Suspension of Remedies: The power of the Supreme Court to issue writs can be suspended during a state of emergency declared by the President of India.
Article 32 is considered to be a cornerstone of the Indian Constitution as it ensures the protection and enforcement of fundamental rights. It enables individuals to directly approach the Supreme Court as a safeguard against any violation of their fundamental rights.
Table of Contents
Superconductors
The origins of superconductivity can be traced back to 1911 when the Dutch physicist Heike Kamerlingh Onnes made a groundbreaking discovery. Onnes, while studying the properties of materials at low temperatures, managed to cool mercury to a temperature of 4.2 Kelvin (-268.95 degrees Celsius), which is just above absolute zero. To his surprise, he observed that the electrical resistance of mercury suddenly vanished, marking the first documented observation of superconductivity.
A major breakthrough occurred in 1957 with the discovery of a new class of superconducting materials called Type II superconductors. Unlike the previously known Type I superconductors, Type II materials exhibited a mixed state in which they could partially resist magnetic fields. This finding opened up new possibilities for applications of superconductivity, as it allowed for the creation of superconducting magnets capable of producing powerful magnetic fields.
Another significant development came in 1986 when two IBM scientists, Karl Alex Müller and Johannes Georg Bednorz, discovered a high-temperature superconductor. They found that a copper-based ceramic material called a cuprate compound could exhibit superconductivity at a temperature of 35 Kelvin (-238.15 degrees Celsius). This breakthrough shattered the long-held belief that superconductivity could only occur at extremely low temperatures and sparked an explosion of research into high-temperature superconductors.
Superconductors are a special class of materials that exhibit zero electrical resistance when cooled below a critical temperature. In other words, they allow for the flow of electric current without any energy loss due to resistance. This phenomenon is known as superconductivity.
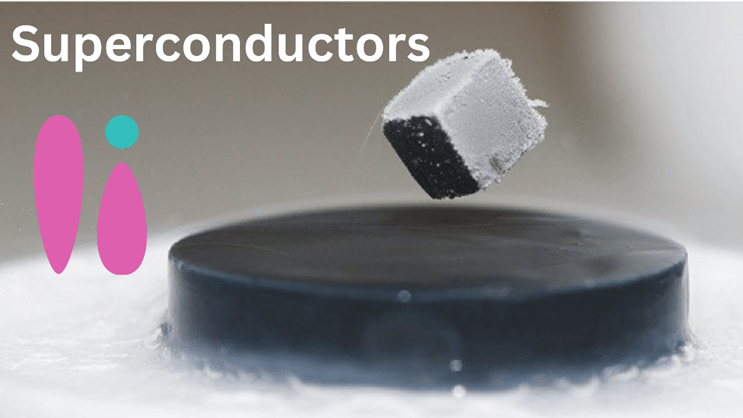
Superconductors also have the unique property of expelling magnetic fields from their interior, a behavior called the Meissner effect. When a superconductor is subjected to a magnetic field, it generates an equal and opposite magnetic field, effectively repelling the applied field and causing the material to levitate or float above a magnet, a phenomenon known as magnetic levitation.
The critical temperature at which a material becomes superconducting varies depending on the specific material. In conventional superconductors, such as certain metals and alloys, the critical temperature is typically very low, ranging from a few Kelvin (close to absolute zero) to a few tens of Kelvin.
Superconductors possess several unique properties and advantages that make them valuable in various fields. Some key properties of superconductors include:
- Zero electrical resistance: Superconductors can carry electrical currents without any loss of energy due to resistance. This property makes them highly efficient for applications involving electrical power transmission and high-performance electrical devices.
- Meissner effect: Superconductors expel magnetic fields from their interior, allowing for the creation of powerful and stable magnetic fields. This property is utilized in applications such as superconducting magnets for particle accelerators, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) machines, and magnetic levitation systems.
- Critical magnetic field: Superconductors can withstand a certain level of external magnetic field before they transition from the superconducting state to a normal conducting state. This critical magnetic field is a crucial parameter for determining the practicality and performance of superconducting materials.
- Flux pinning: Superconductors can trap magnetic flux lines within their structure, a phenomenon known as flux pinning. This property helps to stabilize the superconducting state and allows for the creation of strong and persistent magnetic fields.
- Josephson effect: Superconductors exhibit a phenomenon called the Josephson effect, where a supercurrent can flow between two superconductors separated by a thin insulating barrier. This effect is utilized in superconducting quantum interference devices (SQUIDs) and high-precision sensors.
The study and development of superconductors continue to advance, with ongoing research aimed at discovering new materials with higher critical temperatures and exploring their applications in various fields such as energy transmission, computing, and medical technologies.
India and NATO

NATO, the North Atlantic Treaty Organization, is a political and military alliance established in 1949. It consists of 30 member countries, primarily in North America and Europe, who have agreed to collective defense and cooperation. The alliance aims to promote stability, security, and peace in the North Atlantic region.
India, on the other hand, is a sovereign country located in South Asia. It is not a member of NATO but maintains a significant geopolitical presence in the region. India pursues its own foreign policy goals and has engaged in strategic partnerships and collaborations with various countries and regional organizations.
While NATO and India do not have a formal alliance, there have been interactions and cooperation between India and NATO member countries on specific issues. For instance, India has engaged in dialogue and joint military exercises with NATO members to promote military cooperation and enhance interoperability.
India’s engagement with NATO primarily focuses on areas such as counter-terrorism, maritime security, and peacekeeping operations. There have been instances of information sharing, capacity-building programs, and discussions on regional security challenges. India has also participated in NATO-led operations, including peacekeeping missions in the Balkans and Afghanistan.
It’s worth noting that India follows a policy of non-alignment and prioritizes maintaining strategic autonomy in its foreign relations. As such, while India engages with NATO and other international partners, it seeks to balance its relationships and avoid formal alignment with any particular military alliance.
“NATO Plus five” refers to a grouping that includes the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) and five countries: Australia, New Zealand, Japan, Israel, and South Korea. The purpose of this group is to enhance global defense cooperation and collaboration.
If India were to become a member of NATO Plus, it could potentially benefit in several ways:
- Seamless intelligence sharing: India would have access to enhanced intelligence sharing among the member countries. This would provide valuable information and insights, contributing to India’s national security and counterterrorism efforts.
- Access to advanced military technology: Membership in NATO Plus would give India the opportunity to access the latest military technology and equipment from the member countries. This access could be expedited, reducing the time lag typically associated with acquiring advanced defense systems.
- Strengthened defense partnership with the United States: Joining NATO Plus would further solidify India’s defense partnership with the United States. The United States, being a NATO member, would potentially deepen its military cooperation with India, leading to increased defense collaboration and strategic alignment.
It’s important to note that NATO Plus is a hypothetical scenario, and India’s actual foreign policy decisions regarding alliances and partnerships are determined by a range of factors, including its own strategic interests, regional dynamics, and maintaining its policy of non-alignment. Overall, while NATO and India do have some areas of cooperation and dialogue, their relationship is not characterized by formal alliance membership. Instead, India maintains its own independent foreign policy and engages with various countries and organizations based on its national interests.
Rethinking the Retention of Sedition Law in India

The Law Commission of India, in its 279th report released in April 2023, has recommended retaining Section 124A of the Indian Penal Code (IPC), which deals with the offense of sedition. This recommendation comes in response to the Supreme Court of India’s directive in May 2022 to put all pending sedition cases on hold, citing concerns about the compatibility of the section with the current social milieu. The Law Commission argues that retaining the sedition law is necessary to counter threats to India’s internal security. However, there are contrasting views on the effectiveness and potential misuse of this controversial law.
- Maoist Violence and the Need for Stringent Measures: The Law Commission’s report highlights the violence perpetrated by Maoist groups in India and emphasizes the need to tackle this threat effectively. Data from the Ministry of Home Affairs reveal that Maoist incidents have ranged from 1,533 in 2004 to 509 in 2021, with fatalities varying from 566 to 147 during the same period. The Maoists’ objective is to overthrow the democratically elected government through an armed struggle, posing a significant challenge to internal security. The Law Commission argues that retaining Section 124A IPC provides a legal tool to counter this threat.
- Limited Use of Sedition Law in Maoist Cases: Despite the prevalence of Maoist violence, the Law Commission’s report highlights the minimal use of Section 124A IPC in combating Maoism. In Chhattisgarh, a state heavily affected by Maoist activities, the number of cases registered solely under this section was negligible. Between 2014 and 2021, there were no cases registered under Section 124A IPC in 2015, 2016, 2017, and 2020, and the numbers varied from one to a maximum of three in the remaining years. Instead, provisions under the Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Act (UAPA), the Explosive Substances Act, IPC, and state-specific laws like the Chhattisgarh Special Public Safety Act, 2005, are commonly employed to curb unlawful activities by Maoists, considering their use of improvised explosive devices (IEDs) and ambush attacks.
- Objective Definition of ‘Unlawful Activity’ under UAPA: The Law Commission draws attention to the provision of ‘unlawful activity’ under Section 2(1)(o) of the UAPA, which includes actions intended to cause disaffection against India. The punishment prescribed under this provision is imprisonment up to seven years and a fine. The Supreme Court has consistently held that criticizing the government does not constitute sedition. Comparatively, the UAPA’s definition of ‘unlawful activity’ seems more objective and less problematic than Section 124A IPC. To address any hurdles related to prosecution under the UAPA requiring central government sanction, the Law Commission suggests amending Section 45 of the UAPA to authorize state governments to grant prosecution sanction.
- Lessons from the United Kingdom: The Law Commission’s report cites the example of the United Kingdom, which abolished its law on sedition in 2009. The UK justified the decision based on the availability of a sufficient range of other offenses and the political nature of the offense. The Indian scenario is not significantly different from the UK’s, raising questions about the necessity of retaining Section 124A IPC.
- Conflict with Established Jurisprudence: The Law Commission’s recommendation for conducting a preliminary inquiry to determine prima facie evidence supporting allegations of sedition conflicts with established jurisprudence, as outlined in the Supreme Court’s Lalita Kumari v. Govt. of Uttar Pradesh and others (2014) case. The Supreme Court has ruled that if information discloses the commission of a cognizable offense, the officer-in-charge must register an FIR and initiate an investigation. Preliminary inquiries are permissible only when a case does not clearly disclose the basis of a cognizable offense. The introduction of provisions mandating preliminary inquiries and seeking permission from the central or state government before registering an FIR may be challenged as arbitrary under Article 14 of the Constitution.
Conclusion
Given the contentious nature of the sedition law, it is essential for all state governments and political parties to engage in comprehensive and inclusive deliberations on the Law Commission’s report. Seeking public opinion can help arrive at a more participative and agreeable decision, even if unanimity is not feasible. Balancing the preservation of democratic principles and addressing the country’s security concerns is of utmost importance in determining the future of the sedition law in India.
Gati Shakti Scheme

The Government of India has launched the transformative Gati Shakti scheme, also known as the National Master Plan for multi-modal connectivity. This ambitious initiative seeks to accelerate infrastructure development, reduce logistics costs, and attract private capital investments. Recently, the Confederation of Indian Industry (CII) and various industries have expressed their interest in gaining access to the PM Gati Shakti portal.
Gati Shakti Scheme: Objectives and Integration:
The primary aim of the Gati Shakti scheme is to ensure integrated planning and execution of infrastructure projects over the next four years. It focuses on expediting work, reducing costs, and generating employment opportunities. The scheme incorporates the National Infrastructure Pipeline, a project worth Rs 110 lakh crore, initiated in 2019. By integrating the pipeline, the scheme ensures continuity and comprehensive planning for infrastructure development.
Key Objectives of the Gati Shakti Scheme:
- Reducing Logistics Costs: The scheme targets reducing logistics costs, which will enhance India’s export competitiveness in the global market, foster economic growth, and facilitate trade.
- Enhancing Cargo Handling Capacity: By improving cargo handling capacity, the scheme aims to streamline transportation and logistics operations, enabling efficient movement of goods and reducing bottlenecks.
- Improving Turnaround Time at Ports: The scheme intends to enhance port infrastructure and processes, reducing turnaround time for ships and promoting seamless import and export activities.
- Establishing Industrial and Defense Corridors: The scheme focuses on establishing dedicated corridors for industries and defense, facilitating efficient transportation and promoting economic development in these sectors.
- Extending 4G Connectivity to Villages: With the aim of bridging the digital divide, the scheme seeks to provide 4G connectivity to all villages, enabling access to information, services, and opportunities.
- Expanding Gas Pipeline Network: The scheme aims to expand the gas pipeline network, promoting the use of clean energy sources and fostering sustainable development.
Integrated Approach and Gati Shakti Digital Platform:
The Gati Shakti scheme adopts an integrated approach by bringing together 16 infrastructure-related ministries. This collaborative effort addresses issues related to planning, standardization, clearances, and timely creation and utilization of infrastructure capacities. Additionally, the scheme includes the development of a digital platform, the PM Gati Shakti portal, facilitating real-time coordination and planning of infrastructure projects among various ministries and departments.
Expected Outcomes:
- Mapping of Connectivity Projects: The scheme aims to map existing and proposed connectivity projects, providing clarity on regional and industrial hub linkages, particularly for last-mile connectivity.
- Holistic Transport Connectivity: By integrating different modes of transport, the scheme supports the “Make in India” initiative and establishes a comprehensive and efficient transport connectivity strategy.
- Enhanced Competitiveness: Reduction in logistical costs will improve India’s export competitiveness, thereby promoting economic growth and expanding international trade.
- Economic Growth and Employment: The development of quality infrastructure is expected to stimulate economic activities, foster sustainable development, and create employment opportunities on a large scale.
Challenges to Address:
While implementing the Gati Shakti scheme, addressing certain challenges is crucial for its success. These challenges include declining credit offtake, lack of private demand, land acquisition delays, and litigation. To ensure long-term success, the initiative should be accompanied by a stable and predictable regulatory and institutional framework.
Conclusion:
The Gati Shakti scheme serves as a catalyst for infrastructure development and private investments in connectivity. By promoting integrated planning, improving logistics, and fostering public-private collaboration, the scheme aims to reduce costs, enhance competitiveness, and drive economic growth. Granting industry access to the PM Gati Shakti portal’s non-sensitive data will further facilitate planning and attract much-needed private capital investments, strengthening India’s infrastructure backbone. The successful implementation of the Gati Shakti scheme will not only transform India’s connectivity but also contribute to the overall development and prosperity of the nation.
Kandela IAS recognizes the value of keeping abreast of current events and offers a diverse range of courses to help you stay informed of the latest developments and trends. Kandela IAS team of experienced faculty members is committed to delivering top-quality education that equips you with the knowledge and skills necessary to succeed in your profession. Our blog post, “Important Event held on 18th and 19th May,” provides you with valuable information about significant happenings worldwide. Moreover, Kandela IAS provide comprehensive current affairs courses that encompass a broad range of topics, including politics, economics, sports, and entertainment.
So, if you want to achieve your career objectives, enroll in our courses today and take advantage of the learning opportunities we provide. And also Subscribe for our Youtube Channel Kandela IAS For more updates
At Kandela IAS, we understand the importance of staying informed and up-to-date with current events. Whether you are a professional aiming for career growth or an individual seeking personal development, our comprehensive current affairs courses are designed to cater to your needs. We offer a diverse range of topics, including politics, economics, sports, and entertainment, ensuring that you gain a holistic understanding of the world around you.
By enrolling in our courses, you will have access to experienced faculty members who are dedicated to delivering top-quality education. Our faculty brings a wealth of knowledge and expertise, providing you with valuable insights and perspectives on the latest developments and trends. Through engaging lectures, interactive discussions, and practical exercises, we aim to equip you with the knowledge and skills necessary to succeed in your profession.
Our blog post, “Important Events held on 18th and 19th May,” serves as a preview of the kind of valuable information and insights you can expect from our courses. In this blog post, we highlight significant happenings worldwide during those specific dates. By reading this post, you will get a glimpse of the type of content we cover and the depth of analysis we provide.
To stay even more updated with the latest developments, we encourage you to subscribe to the Kandela IAS YouTube channel. Our YouTube channel offers additional resources, including video lectures, expert interviews, and informative discussions on various current affairs topics. By subscribing, you will have access to a wealth of information that complements our courses, enabling you to expand your knowledge base further.
In today’s dynamic world, it is crucial to be well-informed and adaptable. By taking advantage of the learning opportunities provided by Kandela IAS, you can effectively achieve your career objectives. Whether you aspire to excel in the corporate world, government services, or any other profession, our courses will empower you with the necessary knowledge and skills to navigate the complexities of the modern landscape.
Enroll in our courses today and embark on a journey of continuous learning and growth. Stay informed, stay ahead, and unlock your full potential with Kandela IAS.
